(First, please check our video posted in October 2023 on "Cluneal nerve entrapment" and the "back mice phenomenon")
*We have published a review about back mice: you may access a free on line pdf in the following link → Historical Review of Studies on Sacroiliac Fatty Nodules (Recently Termed “Back Mice”) as a Potential Cause of Low Back Pain. Cañis Parera et al. Pain ther (2021).
In 1951, Barcelona held the Second European Congress of Rheumatology in the faculty of Medicine in Barcelona.
The president was a famous Catalan doctor, professor Agustín Pedro Pons. Pere Barceló Torrent, the founder of the “Secció de reumatologia de l’Acadèmia de Ciències Mèdiques”, was also involved.
Many known rheumatologists went, such as: W. S. C. Copeman, Philip S. Hench (Nobel Prize in Medicine, 1950, from Mayo Clinic in Rochester).
Copeman presided over the Congress and he was also the opening speaker of the session about non-articular rheumatism.
Copeman’s presentation: “Water Retention Syndrome”
In the book II Congreso Europeo de Reumatología. 24-25 septiembre, 1951. Barcelona. Ponencias oficiales, the presentation that Copeman gave at the congress in 1951 is written.
It was titled “Non-articular rheumatism” and the “Water retention syndrome”, signed by Copeman and R. M. Manson.
They come from the Department of Rheumatism, from West London Hospital.
Copeman and Manson start saying that there still exist many unexplained pains that are a real medical problem and are described by the general term of “non-articular rheumatism”.
The terms “non-articular pain” vs. “fibrositis”. Copeman’s prefers the term “non-articular rheumatism”
Sometimes the term “non-articular rheumatism” has to be ceased if a pathological process appears afterwards. But in some other cases, no other alternative appears. Then the term can be used to cover more than one type of painful syndrome.
In recent years, some authors have used the term “fibrositis” but Copeman thinks that the term leads to controversy since the term suggests a fibrotic condition.
Copeman and Manson PROPOSE a new hypothesis
They mention that NONE of current hypothesis as to the cause of “fibrositic” pain is adequate. They propose a NEW CLINICAL SYNDROME to explain the “fibrositic pain”.
They also refer to the term “panniculitis” as being erroneously used.
Current hypothesis: FIBROSITIC
Based on the work of Stockman, who studied the “rheumatic nodules” and found an inflammatory hyperplasia of the white fibrous tissue (with fibroblast but NO LEUCOCYTIC reaction). Stockman thought it could be the result of an infection but couldn’t prove it. Copeman doubts that the lesion is related to undetected focus of infection but rather to past history of rheumatic fever or strain or trauma.
The pain of the fibrous nodule can be referred quite diffusely to anywhere (with the deep neural segment). And it is sometimes erroneously attributed to the joint itself.
The fibrositic nodules are usually located at the tendinous portions or the fibrous aponeurosis of the affected muscles.
Firm pressure elicits an exquisite tenderness and may reproduce the referred pain.
The observations related to febrile processes
Copeman (1943) observed that during the course of several febrile illnesses (influenza, measles, rubella and mumps) “trigger points” of pain could be localized. They become painless as the patient becomes apyrexial, but some remain latent and tender on pressure. They can be reactivated later by occurrence of a fever process, trauma, and temperature changes… and be the basis for “fibrositic” trouble in later life.
Kellgren Ball (1950) also points out the tendon nodules of the rheumatoid arthritis that show NOT SPECIFIC PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES.
Current hypothesis: localized muscle fiber spasm
Based on the recent electromyographic studies, it seems established that certain palpable tender “fibrositic” nodules may constitute localized muscle fiber spasm. The condition presumably results from IRRITATION of the posterior nerve roots by minor lesions in or around the spinal cord (such as developmental defects, arthritis of intervertebral joints, or a mild disc lesion). They may disappear as a result of heat, massage, or local injection of procaine.
Other hypotheses
Psychogenic rheumatism: This is the aching pain in psycho-neurotic individuals. Nodules do no refer it. It usually occurs in the tendinous insertions of certain muscle groups as the result of constant tension or spasm, secondary to their state of mental tension.
Toxaemia: Chronic muscular pain may occur as the result of infected focus such as sinusitis. During acute infection or sub-acute or chronic phase.
Others: Microtrauma (minor but repetitive trauma), severe cold and hot, unaccustomed exercise.
Fibro-fatty tissue in relation to non-articular rheumatism
In addition to the fibrous and muscular tissues, there is a third tissue, fat, also of mesodermal origin. Copeman and Mason think that fat tissue has to be considered as a cause of pain in the category of non-articular rheumatism.
Fatty tissue is widely distributed in the body. In addition to being protective, it appears to be functional, and one of its chief physiological functions is concerned with the storage of body water.
The derangement of its normal function of water-storage would lead to a PAINFUL FIBRO-FATTY TISSUE DISTENTION SYNDROME.
The term “panniculitis” has partly been used to explain this syndrome. Nevertheless, Copeman and Manson state that since no evidence of an inflammatory pathology exists (except in TRUE panniculitis), it is better to use the term “water retention” or briefly “tension syndrome”.
“Water Retention Syndrome” or “Tension Syndrome”
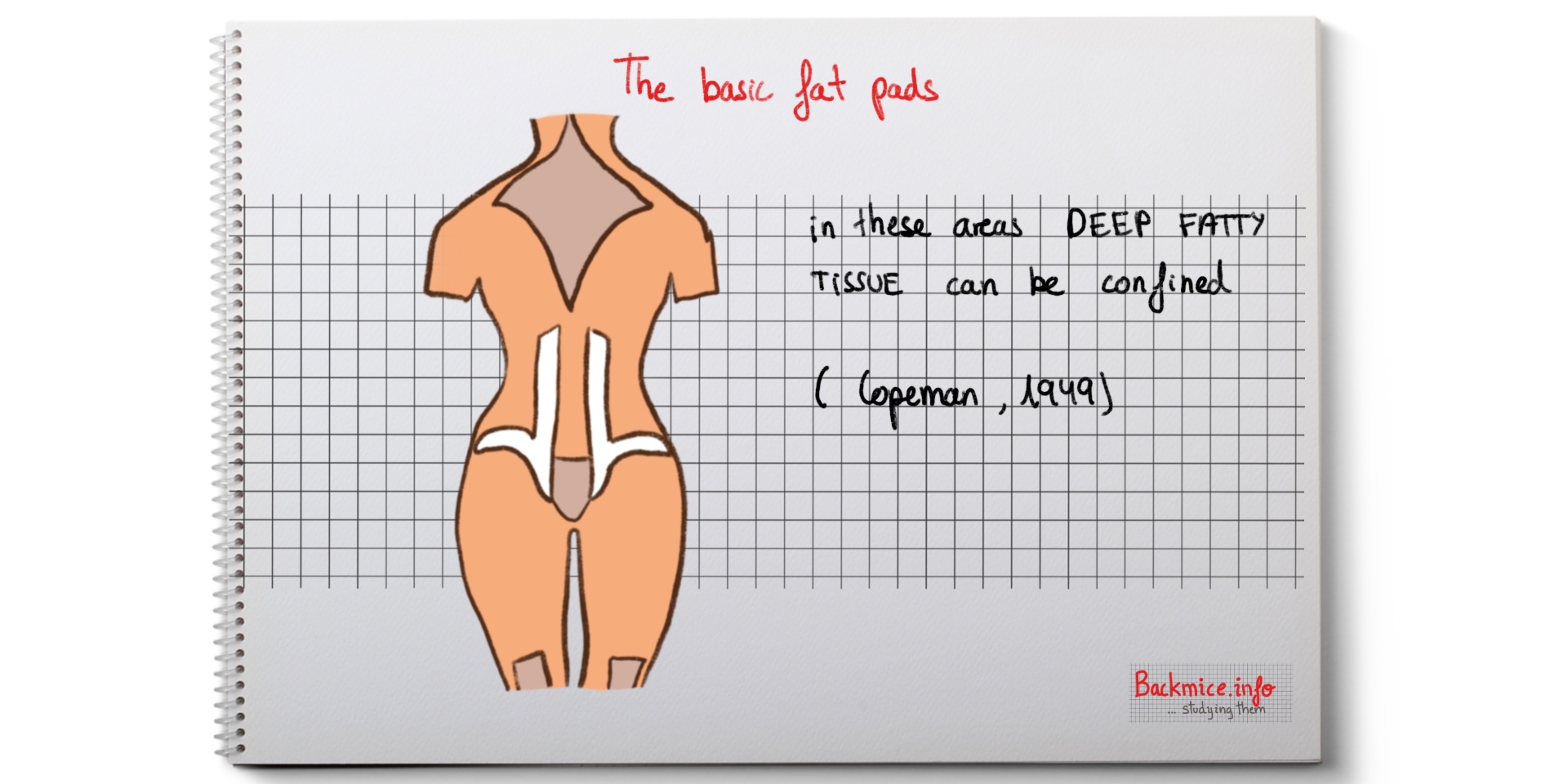
This is a painful condition caused by periodical swelling of the deep fatty tissue in certain well-defined sites of the body where the affected FAT LOBULES are confined by an unyielding or thickened fibrous covering.
Local tension results in pain. It is generally diagnosed as “fibrositis” in view of the lack of objective signs or sometimes as “psychogenic” rheumatism.
Onset of the “Water Retention Syndrome”
-It occurs principally in women, it can be associated to a recent increase in weight (although the victim doesn’t need to be obese).
-Its onset can be within the menopause zone or subsequent to an artificial menopause.
-Long periods of freedom from pain are not unusual.
-Sometimes it occurs only during the few days preceding the monthly menstrual period. If the patient were in menopause, at such time as when menstruation would have otherwise occurred.
-The onset of attacks is often unexpectedly acute; it usually passes off less suddenly than it occurs.
Symptoms of Copeman’s “Water Retention Syndrome”
-The general health of the patient is preserved except for the “mental depression” secondary to a prolonged attack.
-There may be disturbed sleep either by the stiffness or by pain lying on the tender area.
-A feeling of lassitude or irritability precedes some attacks.
-The patient often describes a sensation of generalized swelling of the body and limbs, in addition to that experienced as pain in certain regions (the size of the fingers can be shown to be increased, evidenced by the patient’s inability to wear their usual rings).
-Sometimes there is an increase in body weight.
Sites of pain:
-Although the patient described severe pains as diffuse, examination would reveal it to be situated in certain well-defined areas in which the deep fatty tissue is confined by an indistinguishable fibrous fascia. These sites have been shown in a diagram in previous studies.
-The dorsal and the knee fat-pads are usually the most commonly implicated.
-If the sacrum fat-pad is involved, then it may be visible from inspection.
-The skin shows a “peau d’orange” appearance.
-On palpation there are “painful nodules”.
-There can be “trigger points” situated in the fat-pads.
Copeman and Manson’s clinical investigations with patients with “fibrositic pain”
They did 3 types of experiments to try to force or to reduce the body water retention.
–First experiments: Copeman and Manson tried to do experiments by weight reduction and diuretics, without any conclusive result to pain relief.
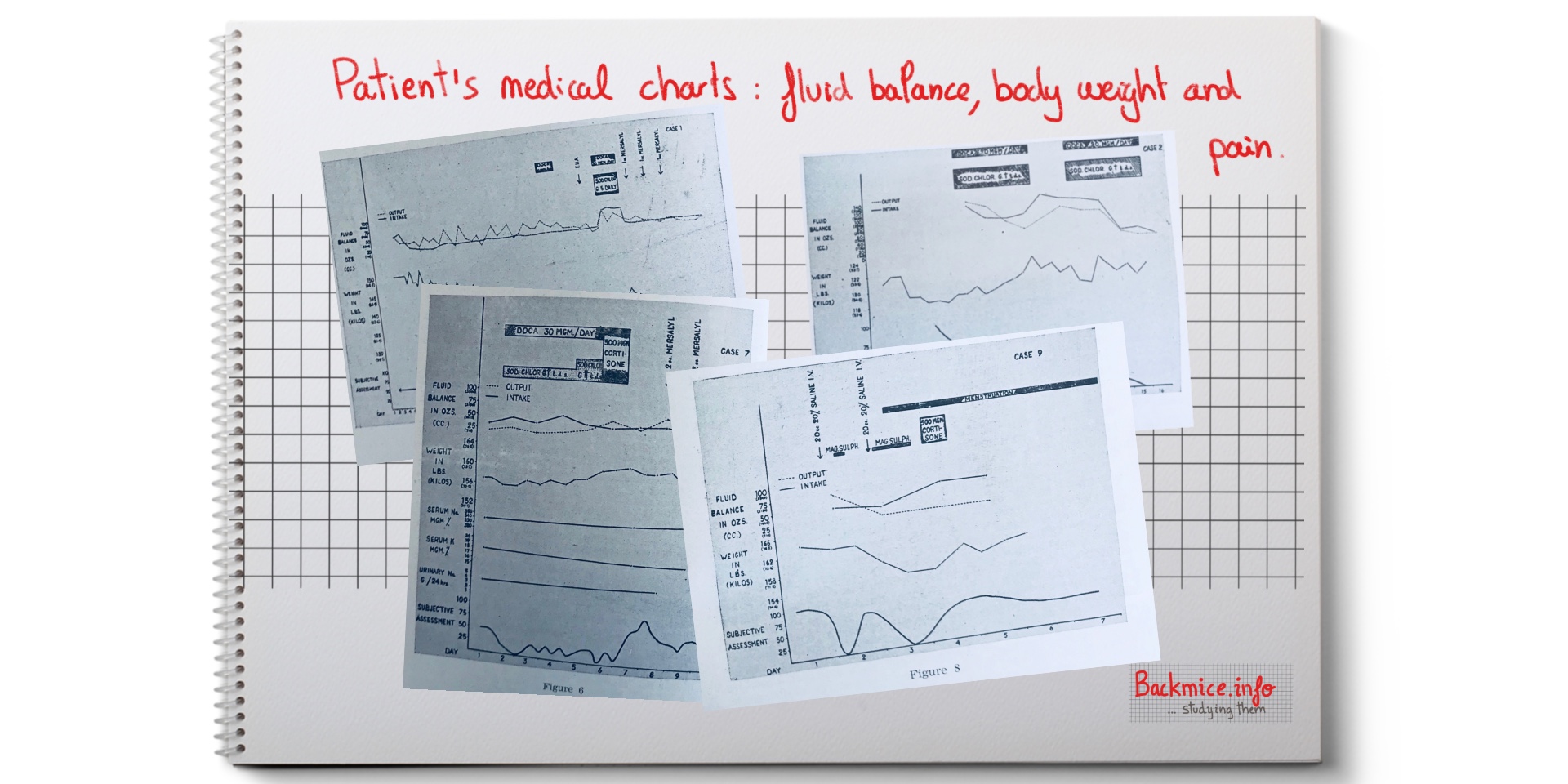
–Second experiments: Later, they tried to induce an artificially “water retention syndrome” with and hormone deoxycortone to induce an attack, which also failed. They explained 5 cases. And they showed the fluid balance, body weight and pain subjective assessment in the clinical charts.
–Third experiments: By chance, they observed a patient who was given cortisone for osteoarthritis; they observed the knee fat pads increased of size. Then they experimented on two cases. They administrated single large intramuscular cortisone dose that exacerbated the pains of the tension syndrome in both patients. Then they experimented by causing INTRACELULAR DEHYDRATATION in two patients by injection of intravenous hypertonic saline, which reduced the pain temporarily. They finally hypothesized cortisone may increase an increased volume in intracellular fluid, and then increase the water retention syndrome.
One of the cases was Case 1. Woman, 24 years old. Severe lumbar backache for six years. Pain all over the lumbar region fluctuating in severity but always present. Pain did not radiate to legs. No lumbar spine lesion was found. Four years before, an iliac fatty hernia was removed, which relieved her pain. However, pain recurred more generally and she was admitted to hospital. On examination MULTIPLE EXQUISITELY TENDER NODULES could be felt over both iliac crest. X-ray revealed no changes. The experiments they did on her didn’t have any effect on her pain.
Published in April 2018 By Marta Cañis Parera 
References:
- Book II Congreso Europeo de Reumatología. 24-25 septiembre 1951. Barcelona. Ponencias oficiales. Editorial Publicaciones Médicas José Janés Editor. Cuarta ponencia: Reumatismo no articular y síndrome de retención de agua. W. S. C. Copeman. Páginas 209-228
- Copeman W. S. Aetiology of the Fibrositic Nodule. Br Med J. 1943 Aug 28; 2(4312): 263-4. PubMed PMID: 20785002; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2284845.
- Copeman W. S. C. Fibro-fatty Tissue and its Relation to “Rheumatic” Syndromes. British Medical Journal. 1949; 2(4620): 191-197.






The Guaifenesin Protocol by Dr. R. Paul St. Amand proposes that in Fibromyalgia, these “mice” are nodules caused by an inherited enzyme defect, that then causes a lifetime of phosphate and calcium retention, eventually forming these mysyerious lumps as the minerals get pushed into cells. Current FM/CFS reversal success rates are extremely high over time, using this 50 year-old-protocol precisely, and the lumps disappear systematically in time. A very safe OTC treatment, the Guaifenesin Protocol has saved many FM/CFS folks I know from disease progression, including myself. It is not a cure, but over time, when used with care, it reverses all symptoms (and eliminates most mice!)